 |
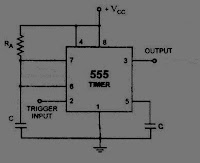
| Multivibrator Monostable IC 555 |
level. The time taken in storage determines the pulse width. The transition of output from stable state to quasi-stable state is accomplished by external triggering.
Capacitor C has to charge through resistance RA. The larger the time constant RAC, the longer it takes for the capacitor voltage to reach +2/3VCC. In other words, the RC time constant controls the width of the output pulse. The time during which the timer output remains high is given as
tp = 1.0986 RAC
where RA is in ohms and C is in farads. The above relation is derived as below. Voltage across the capacitor at any instant during charging period is given as
vc = VCC (1- e-t/RAC)
Substituting vc = 2/3 VCC in above equation we get the time taken by the capacitor to charge from 0 to +2/3VCC.
So +2/3VCC. = VCC. (1 – e-t/RAC) or t – RAC loge 3 = 1.0986 RAC
So pulse width, tP = 1.0986 RAC s 1.1 RAC
The pulse width of the circuit may range from micro-seconds to many seconds. This circuit is widely used in industry for many different timing applications.